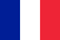
Chronic prostatitis is an persistent inflammation caused by an infection or pathology in the prostate gland.
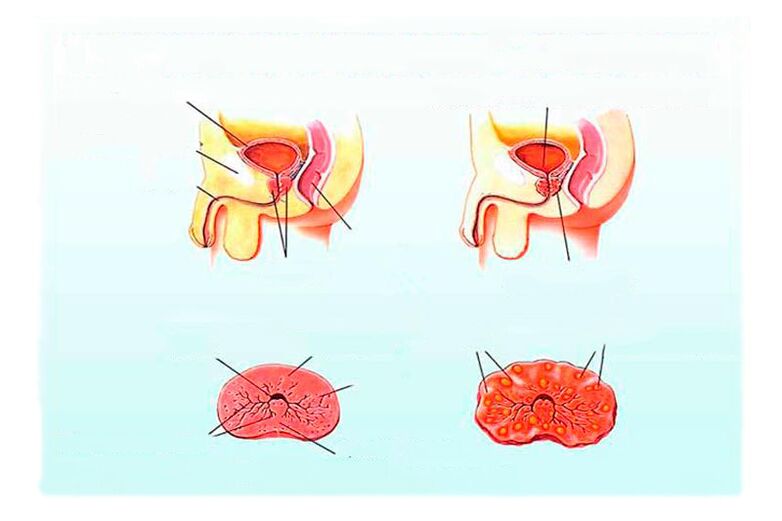
Chronic prostatitis is diagnosed in men of all ages.According to statistics, the disease is the most common cause for visits to urologists in patients under the age of 50.In chronic form, bacteriological examination reveals pathogens in only 5-10% of patients.In most cases, other factors are considered the cause of the disease.It is known that the presence of infection is not a prerequisite for the occurrence of the disease.Chronic inflammation of the prostate is a polyTiological pathology, which is the result of the action of several provocative causes and factors.In 90-95% of patients, antibacterial therapy has limited or unnecessary effectiveness at all.
Classification of chronic prostatitis
Chronic prostatitis classification by etiological characteristics distinguish between two main forms of the disease: chronic (contagious) prostatitis and non -chronic prostatitis (aseptic) prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain (KTS).
Chronic prostatitis etiological classification includes:
- Chronic bacterial prostatitis.
- Prostatitis/non -chronic (aseptic) ("prostatini", or "painful prostate gland" is an outdated term used to determine pathology).
- Non -chronic (aseptic) prostatitis with inflammatory components (leukocyte concentration increases significantly in prostate secrets, sperm, first part of urine).
- Prostatitis/CTB Non -chronic (aseptic) without inflammatory components (white blood cell concentration in prostate secrets, sperm, the first part of urine is not sufficient for inflammation).
- Chronic prostatitis Ashmptomic (detected in laboratory studies, not clinically manifested).
Chronic bacterial prostatitis is a rare pathology, as can be seen from the above statistics.Infection is the cause of recurrent inflammation of the prostate in one in ten patients.Pathology is often associated with other infectious diseases of the genitourinary organ.Often, the cause is a non -specific infection, however, with the presence of STSPP, chronic inflammation of the gland can be caused by chlamydia, uraplasmosis, mycoplasmosis or other microorganisms.
Non -chronic (aseptic) prostatitis, or chronic pain syndrome, is a long recurrent disease caused by prostate aseptic inflammation.This is a small pathology.With the presence of symptoms of the disease, the test of white blood cells in the secret of the gland, in the seed fluid, in the early part of the urine, but the results of the bacterial examination are negative.In other cases, there are no signs of infection, or leukocytosis mentioned with bright symptoms.
There are also chronic prostatitis in the exacerbation and chronic prostatitis in the remission phase.Cycle courses are the second features of bacterial inflammation and not prostate gland.Increased chronic prostatitis leads to increased symptoms in both cases.
Pathanatomical (pathomorphological) chronic prostatitis classification is limited to patients and clinic doctors.
The cause of chronic prostatitis
Causes of Chronic Bacterial Inflammation of Prostate gland
Chronic infectious prostatitis is caused by an infection of the prostate gland tissue.Often, the cause of inflammation is E. coli, or E. coli.Microbes are less carved from the genus enterococci, klebsell, proteus, pseudomonas.
Like some other microbes, E. coli is capable of forming biofilm, thin, consisting of bacterial and tight accumulation next to the mucous membranes of the channel.This explains why it is not always possible to cure chronic prostatitis.It is believed that the infection spreads as an ascending way through the urethra.However, the spread of lymphogenic and hematogen infections is also possible.
The predisposition factor for the occurrence of chronic infectious prostatitis is as follows:
- Sexually active age;
- prostate adenoma, or benign prostate hyperplasia;
- narrowing the urethra;
- Open the extreme meat of the penis;
- Hypertrophy of bladder neck;
- medical procedures (bladder catheterization, cystoscopy);
- Characteristics of genetic and predisposition of the disease to the disease.
Causes of non -chronic inflammation of the prostate gland
The cause of non -chronic prostatitis is unknown.The disease may be caused by a virus or bacteria, which is not identified during the secretion of the prostate gland bacteria.However, most scientists and doctors believe that non -chronic (aseptic)/CTB prostatitis is a polyetiological disease caused by a combination of several bad factors, namely:
- cycling;
- irritation of the prostate gland tissue when the urine enters its channel;
- prostate gland irritation as a result of the use of products or beverages (especially with food allergies or celiacia);
- functional disorders of the nerve monitoring of the pelvic organs;
- Pelvic floor muscle atrophy;
- pressure, psychoemotional load;
- Pathology in the prostate gland, which remains after the old acute prostatitis;
- hormone disorders;
- bladder disease;
- Cold climate.
Due to the true cause of the disease, the treatment of chronic prostatitis can be difficult.
Symptoms of chronic prostatitis
Chronic bacterial prostatitis (contagious) is characterized by a cycle course.The exacerbation phase is replaced by the pardon phase.There are almost no symptoms between severity.There is a clear relationship between other diseases of the genitourinary organs - urethritis, epididymmets, cystitis.The cause of this pathology, as a rule, is the same pathogen that causes chronic prostatitis.Symptoms during oppression are represented by dysuric phenomena (frequent urination, rubber and burning pain during urination) and pain with various intensity in the perineum, scrotum, sacrum, with radiation in the penis.
General conditions are usually satisfactory.No signs of intoxication, no increase in body temperature.The prostate gland when examining through the rectum (per rectum) can be normal or slightly swollen, without the acute prostatitis.
Non -chronic prostatitis/KTB (aseptic) is characterized by different pains -different levels of severity (from stupid to intense) in the pelvis, perineum, sacrum and "visitor card" disease (aseptic chronic prostatitis).The signs of inflammation of the prostate gland are not well stated and are observed in 50% of cases.In other patients, they may not be present.
The presence of blood in sperm, painful ejaculation, water removal, dysouric phenomenon may be.Symptoms may change.The pain is given to the throat, the rectum, making it difficult to find someone in a sitting position.Fatigue, unreasonable fatigue, articular and muscle pain are also possible.Some patients complain of decreased sex drive, erectile dysfunction (impotence).
Chronic prostatitis without symptoms has no characteristic of the symptoms of the disease, so its name is.During a prostate secret laboratory study, leukocytosis is determined, an increase in certain prostate antigen levels.There are no other signs of illness.
Diagnosis of chronic prostatitis
The main method for diagnosing chronic infectious prostatitis is a laboratory and topical tests that allow you to know the source of leukocytes in urine and sperm.
Three -time urine tests help identify inflammation.To do this, the patient removes three containers for analysis.The prostate massage between the second and third containers leads to the stimulation of the gland secretion.As a result, urine in the third container will contain the release of the prostate gland (leukocytes, red blood cells, bacteria), which is determined during analysis.No need to massage special prostate and explore the secrets of the gland.
Urine from the third container can be sent to the bacterial examination by sowing to the nutrient medium.In the presence of bacterial growth, tests are conducted for pathogenicity to antibiotics.This method helps to perform the treatment more accurately and effectively.Because prostatic secrets are a major part of the sperm, microscopy and ejaculation bacteria also make it possible to make the right diagnosis.
Chronic bacterial prostatitis (contagious) is accompanied by a slight increase in PSA.The level is reduced after successful treatment.Ultrasound and other instrumental studies have no significant diagnostic value.
Diagnosis of chronic non -chronic (aseptic) prostatitis can be difficult.Usually diagnosis is made by excluding other pathologies of genitourinary tract and bacterial prostatitis.For this, the instrumental and laboratory methods are used: urine microscopy (three -fold tests are also used after prostate massage), sperm or prostate secret, followed by sowing nutrient medium.The list of studies includes analysis for PSA (diagnosis of cancer differentiation and prostate inflammation).
Microscopy reveals the presence of leukocytes in urine, in prostate secret, seed fluid with negative results of bacteriological treatment methods.Instrumental research methods (ultrasound, cystoscopy, MRI, CT) do not reveal the signs of pathology.
Treatment of chronic prostatitis
For successful treatment of chronic infectious prostatitis, rational and targeted antibacterial therapy is required.The choice of choice is fluoroquinolones that produce a large concentration of drugs in gland tissue.The course of treatment takes six to 12 weeks.The duration of such antibacterial therapy is required for the disinfection of the infection and the prevention of complete relapse.The second medicine.
Bacterial chronic prostatitis can be cured with consistent and adequate therapy.Patients with frequent relapse should check your immune status.It is also necessary to exclude HIV infection, which often results in low effectiveness of antibacterial therapy.In such patients, it is possible to prescribe antibiotics at sufficient doses to suppress bacterial growth.
Treatment of non -chronic prostatitis/KTS is difficult, as infection is not the cause of chronic pain in the pelvis or abacterial chronic prostatitis.It is necessary to approach the problem seriously and answer the question of how to treat the disease, the unknown cause.
The absence of certain etiology explains why attempts for this pathological therapy are often unsuccessful.
Chronic aseptic prostatitis treatment methods contain:
- Antibacterial therapy with fluoroquinolones (performed by all patients).It is possible to have an infection that is not detected during bacteriological examination.
- Alpha-blockers.They contribute to increased blood circulation in the prostate tissue.The effectiveness is low.
- NSAIDs and other anti -anticipation drugs have severe efficacy, relieve pain and improve symptoms.However, treatment is pathogenetic, after cancellation, the disease renewal is possible.
- Physiotherapy and physiotherapy exercises (yoga, sports, active lifestyle), help improve blood circulation and eliminate venous stagnation, hypoxia, strengthen pelvic muscles.This method helps patients with appropriate disorders.
- Antidepressants and anticonvulsants (unpredictable).
- Surgical treatment: laser ablation or thin prostate gland (ineffective).
Prophesy
In chronic infectious prostatitis in most patients, prognosis is good.Consistent and adequate antibacterial therapy allows you to succeed in more than 80% of cases.
Chronic non -chronic (aseptic) prostatitis has the worst predictions.Treatment only helps a few patients.Others continue to suffer from chronic pain syndrome, despite using all available treatment methods.The disease has a clear effect on the psycho spheres -emotional and sexual relations.